The car industry’s attempts to eliminate hazardous emissions have become synonymous with catalytic converters. But what happens to these essential parts after their useful lives are over? Recycling catalytic converters is an environmentally friendly and sustainable way to recover priceless precious metals. This essay will explain catalytic converter recycling’s operation and the reasons it’s important for the economy and ecology.
The Workings of Catalytic Converter Recycling
A number of procedures are involved in catalytic converter recycling in order to remove and retrieve valuable metals from the converters:
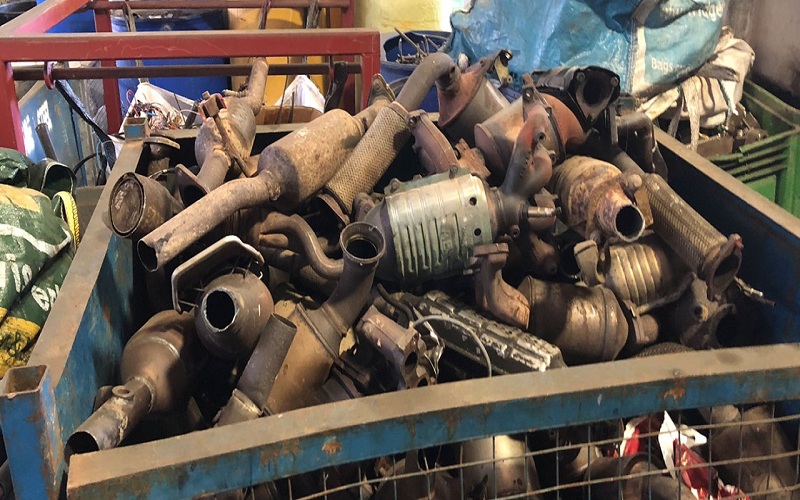
Collecting: Secondhand catalytic converters are gathered from automobile repair shops, recycling facilities, scrap yards, and automobiles nearing the end of their useful lives.
Decanning: The substrate and the precious metal catalyst are made visible by removing the converters’ outer shell.
Crushing/Shredding: To improve the surface area for metal extraction, the substrate—typically composed of metallic or ceramic material—is crushed or shredded.
Recovery of Precious Metals: Different techniques are employed to extract the precious metals from the substrate. These techniques include mechanical extraction, heat processing, and chemical leaching.
Refining: Once recovered, precious metals undergo a refining process to attain high purity levels and eliminate impurities.
Sale and Reuse: Manufacturers purchase refined precious metals to use in fresh catalytic converters or for other industrial purposes.
The Significance of Recycling Catalytic Converters
Recycling catalytic converters is crucial for a number of reasons:
Resource Conservation: Platinum, palladium, and rhodium are just a few of the precious metals found in catalytic converters. Recycling these metals helps protect sensitive ecosystems and natural resources by reducing the need for fresh mining and extraction.
Reducing Pollution: Cars emit fewer hazardous pollutants when their catalytic converters are recycled. By reusing the recovered precious metals in new converters, emission control regulations can be preserved or even raised.
Energy Conservation: Recyclables use less energy than virgin metal mining and processing. Energy utilisation and greenhouse gas emissions related to metal manufacturing are decreased by employing recycled metals.
Economic Benefits: By generating jobs in manufacturing, metal refining, and recycling facilities, catalytic converter recycling boosts the economy. Additionally, it supplies industry with important metals on a consistent basis, promoting stability and economic progress.
Protection of the Environment: Recycling catalytic converters prevents the discharge of dangerous chemicals and pollutants that result from disposing of these devices in landfills. Additionally, it lessens the negative effects of mining on the environment, such as habitat damage and water contamination.
Regulatory Compliance: To encourage the recycling of catalytic converters and guarantee appropriate waste management, some nations have put rules in place. Respecting these rules guarantees that scrap items are handled responsibly and helps stop unlawful disposal.
Conclusion
Recycling catalytic converters is an essential component of the automobile industry’s environmental initiatives. Recycling preserves important resources, lowers emissions, saves energy, boosts the economy, and safeguards the environment by recovering precious metals from converters that have reached the end of their useful lives. Knowing how and why catalytic converter recycling is important emphasises the value of appropriate waste management and the part that each person can play in fostering a cleaner, greener future.